As I partook in my morning repast, a palpable surge of vitality enveloped me. The protein-dense meal, consisting of Greek yogurt, fresh berries, and a sprinkling of almonds, served as the ideal catalyst for my day’s commencement. The profound impact of judiciously selected sustenance on our vitality and efficacy is truly remarkable.
In our contemporary era, adhering to a high-protein regimen is imperative for both physical and mental health. Protein-rich edibles not only facilitate muscle development and restoration but also underpin energy synthesis, cognitive acuity, and longevity. By meticulously curating a diverse array of protein sources, we guarantee our bodies receive the indispensable nutrients requisite for flourishing.

Key Takeaways
- Protein is essential for body function and energy production.
- Choosing unprocessed, protein-rich foods can help fight fatigue and maintain high energy levels.
- A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and complex carbs is key for optimal health and wellness.
- Incorporating a variety of protein sources, both plant-based and animal-based, is recommended for a healthy, high-protein diet.
- Proper timing of protein intake, such as before and after workouts, can maximize the benefits for performance and recovery.
Understanding Protein’s Role in Body Function and Energy
Proteins, the fundamental constituents of the human organism, are indispensable for numerous physiological functions. These intricate molecules, comprising 20 distinct amino acids, include essential components that must be ingested through dietary means. Grasping the significance of these indispensable amino acids and their role in energy metabolism is paramount for sustaining health and physical fitness.
Essential Amino Acids and Their Functions
The nine indispensable amino acids—histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine—are crucial for hormone synthesis, enzyme production, and the formation of immune cells. They are also pivotal for muscle growth and repair. Adequate consumption of protein-rich foods is imperative to fulfill the body’s requirements for these vital components.
How Protein Supports Energy Production
Protein, a critical macronutrient, is instrumental in sustaining energy levels. In the absence of carbohydrates, the body can convert protein into glucose through gluconeogenesis. This transformation of amino acids into glucose serves as an alternative energy source, facilitating physical activity and metabolic processes. Protein intake is essential for maintaining muscle mass and enhancing resting metabolic rate, thereby aiding in weight management and achieving fitness objectives.
Daily Protein Requirements for Different Age Groups
The daily protein intake varies significantly based on age, sex, weight, and activity level. Typically, adults should aim for 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Nonetheless, individuals with higher activity levels, pregnant women, and older adults may require greater protein intake to support muscle recovery, growth, and overall health. Consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable to determine the most suitable protein intake for your specific circumstances and lifestyle.

“A balanced diet that includes a variety of protein-rich foods is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.”
Benefits of High-Protein Diet for Health and Wellness
The inclusion of protein foods for weight loss, protein for muscle growth, protein for weight management, and protein for athletes within a diet regimen offers a multitude of health advantages. A diet rich in protein, when complemented by other vital nutrients, fosters satiety, aids in weight management, and diminishes the likelihood of high blood pressure.
Protein’s role in injury recovery and the prevention of sarcopenia, a condition characterized by muscle mass decline with age, has been substantiated. Additionally, a high-protein diet may contribute to the preservation of cognitive function and support healthy aging, especially when plant-based protein sources are utilized.
“A balanced high-protein diet, combined with regular exercise and proper sleep, can positively impact overall health and wellness.”
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025 advocate for adults to derive between 10% and 30% of their daily caloric intake from protein. Nonetheless, many individuals face challenges in meeting their protein requirements due to the prevalence of carbohydrate-dense, processed foods.
It is crucial to acknowledge that while a high-protein diet can confer numerous benefits, excessive intake may result in adverse effects such as nausea, constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, bloating, weight gain, and dehydration. A diet that emphasizes lean protein, vegetables, berries, and whole grains can optimize benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks.

| Protein Intake Guidelines | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for Healthy Adults | 0.8 g/kg/day |
| Active Adults | 1.2 to 1.7 g/kg/day |
| High-Protein Diet Macronutrient Ratio | 30% protein, 30% fat, 40% carbohydrates |
By meticulously balancing protein intake with other essential nutrients and incorporating regular physical activity, individuals can leverage the advantages of a high-protein diet to support their health and wellness objectives.
Protein-Rich Foods: Complete Guide to Sources
Incorporating a variety of protein-rich foods into your diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health and energy levels. From animal-based to plant-based options, there is a wealth of high-quality protein sources to explore. Let’s delve into the different categories of protein-rich foods and their unique benefits.
Animal-Based Protein Sources
Lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs are exemplary sources of animal-based protein. These foods provide complete proteins, containing all the essential amino acids your body necessitates. Sardines, for instance, pack a powerful 18 grams of protein in a half-cup serving. Chicken breast offers a substantial 27 grams of protein per 4-ounce portion, while canned tuna boasts an impressive 40 grams of protein per can.
Plant-Based Protein Options
For those seeking plant-based protein sources, legumes, tofu, tempeh, and soy products are excellent choices. Lentils, for example, contain 18 grams of protein per cooked cup, while tempeh provides an impressive 33.7 grams of protein per cup. Nuts and seeds, such as peanuts (7.3 grams per ounce) and oats (5 grams per cooked cup), also offer valuable plant-based protein.
Dairy and Alternative Sources
Dairy products, including Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, are rich in high-quality protein. A cup of cottage cheese packs nearly 24 grams of protein, making it a fantastic option. For those with lactose intolerance, dairy alternatives like almond milk and soy milk can provide comparable protein content.
By incorporating a diverse range of protein-rich foods into your diet, you can ensure your body receives the essential amino acids and nutrients it needs to thrive. Whether you prefer animal-based, plant-based, or a combination of sources, there are numerous delicious and nutritious options to explore.

“Protein plays a crucial role in muscle health and recovery, with essential amino acids aiding in muscle repair and the synthesis of new muscle fibers.”
Lean Meats and Poultry for Optimal Energy
Lean meats and poultry stand as paramount lean protein sources, instrumental in fueling the body with vital nutrients for peak energy levels. These protein-packed foods not only deliver high-quality protein but also a plethora of other essential vitamins and minerals.
A 3-ounce serving of 93% lean ground beef boasts an impressive 22 grams of protein, while a 3-ounce serving of skinless chicken breast offers a substantial 27 grams of protein. These high-protein foods are also rich in nutrients like zinc and iron, critical for maintaining energy and supporting overall health.
Incorporating lean meats and poultry into your meals can revolutionize your energy levels throughout the day. The combination of high-quality protein, essential nutrients, and minimal fat content makes these protein sources an optimal choice for those seeking to fuel their bodies with the nutrients they need.
“Lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of red meat are essential for building and maintaining muscle mass, which is key for powering through your day with energy and vitality.”
Whether you’re an athlete, a busy professional, or simply someone looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle, lean meats and poultry should be a staple in your diet. Experiment with different preparation methods, such as grilling, baking, or sautéing, to keep your meals exciting and nutritious.
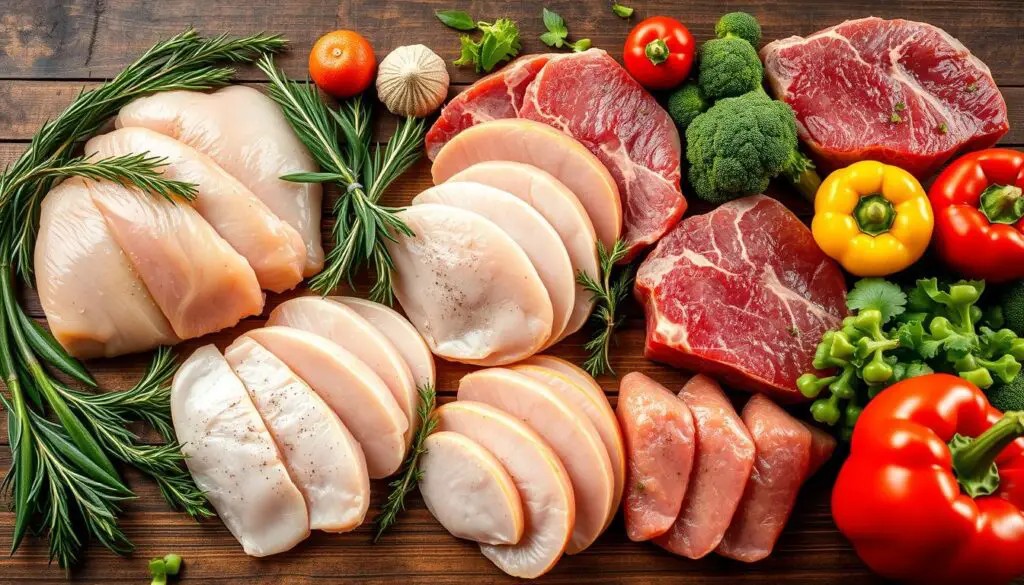

Remember, the USDA defines lean protein sources as those with less than 10 grams of total fat, 4.5 grams or less of saturated fat, and less than 95 milligrams of cholesterol per 100 grams of cooked meat. By focusing on these lean protein sources, you can enjoy the benefits of high-quality protein without compromising your overall health and wellness.
Fish and Seafood: Premium Protein Sources
In the realm of dietary protein, fish and seafood emerge as unparalleled options. These high-protein foods not only facilitate muscle development and recovery but also offer substantial energy-boosting advantages.
Fatty Fish Benefits
Cold-water fatty fish, including salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are distinguished by their abundance of omega-3 fatty acids. These acids possess potent anti-inflammatory properties and contribute significantly to cardiovascular health. A 3-ounce portion of salmon, for example, contains approximately 22 grams of premium protein.
Regular consumption of fish, particularly the fatty varieties, at least twice weekly, ensures a comprehensive intake of vital nutrients. These include vitamin D, selenium, and B vitamins, all of which are pivotal for maintaining energy levels and overall well-being.
Sustainable Seafood Choices
- When selecting seafood, prioritizing sustainability is crucial. Seek out options certified by entities such as the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) or Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC). These certifications guarantee adherence to responsible fishing and farming standards.
- Wild-caught fish, when obtained responsibly, represent a sustainable choice. Similarly, well-managed farm-raised fish can help mitigate the strain on wild populations and reduce habitat destruction.
- Prefer cooking methods like baking, steaming, and grilling to maintain the nutritional value of your fish and seafood.
By integrating a variety of protein-rich, energy-boosting fish and seafood into your diet, you can partake in the advantages of a well-balanced, healthy lifestyle.
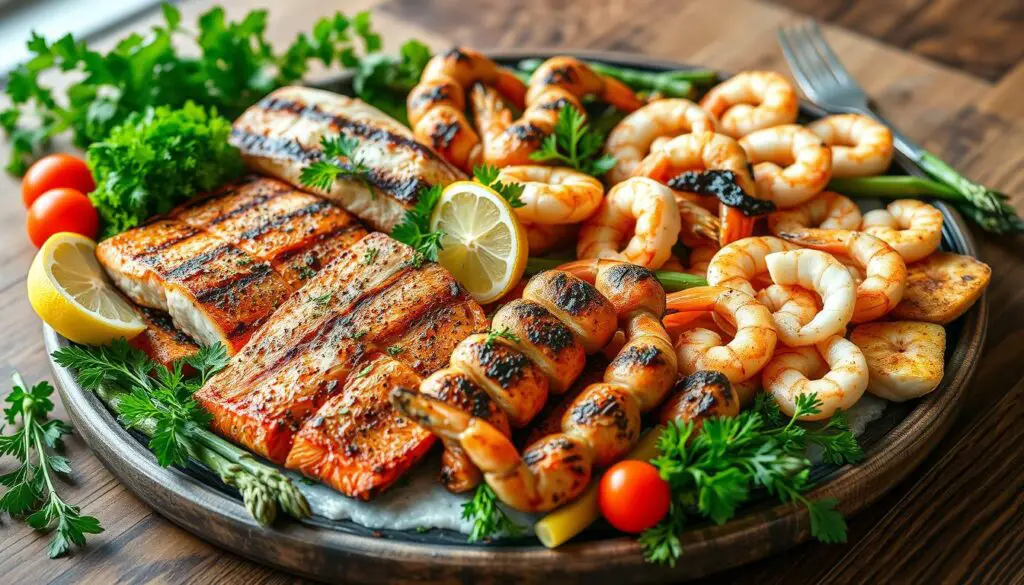
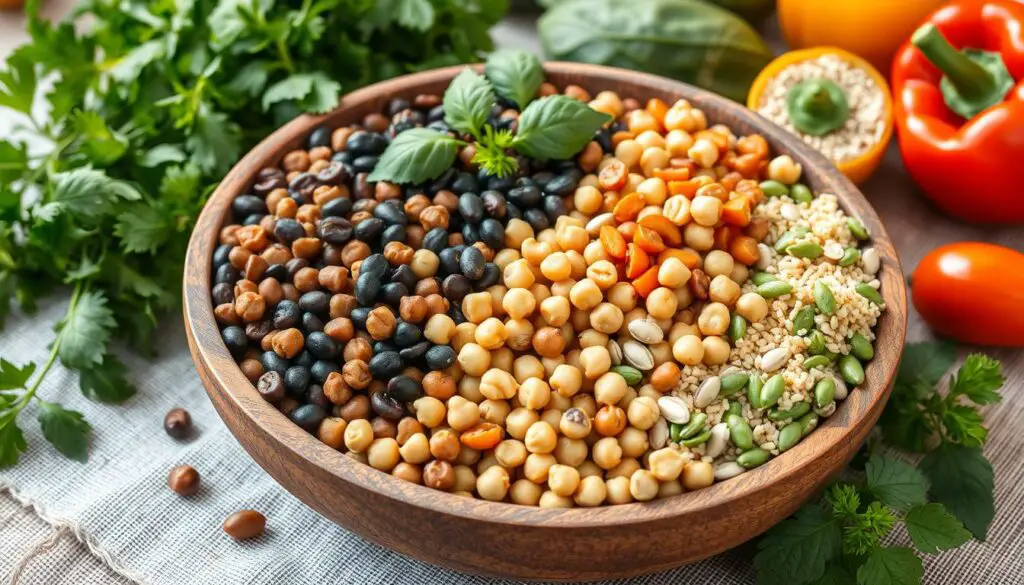
Plant-Based Protein Powerhouses
Exploring the realm of plant-based protein reveals a plethora of options for those desiring to augment their dietary intake. Vegetarian protein sources such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, and seitan are replete with nutrients and health advantages. Lentils, for example, boast an impressive 18 grams of plant-based protein per cup when cooked, positioning them as an exemplary choice for those in pursuit of a high-protein vegetable.
Extending beyond legumes, a myriad of vegetarian protein sources exists, each capable of supporting muscle growth, weight management, and overall health. Chickpeas, for instance, contain approximately 7.5 grams of protein per half-cup serving, while hemp seeds offer around 10 grams of protein in just 3 tablespoons. Tofu, a versatile plant-based protein, contributes 9 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving.
| Food Item | Protein Content |
|---|---|
| Lentils (1/2 cup cooked) | 9 grams |
| Chickpeas (1/2 cup cooked) | 7.5 grams |
| Hemp Seeds (3 tablespoons) | 10 grams |
| Tofu (3 ounces) | 9 grams |
| Nuts (1/4 cup) | 5-6 grams |
| Quinoa (1 cup cooked) | 8 grams |
| Nutritional Yeast (1/4 cup) | 8 grams |
| Tempeh (3 ounces) | 14 grams |
By integrating diverse plant-based protein sources, one can achieve a comprehensive amino acid profile, crucial for vegetarians and vegans. Incorporating these high-protein vegetables and vegetarian protein sources into one’s diet facilitates the enjoyment of a protein-rich, plant-based lifestyle’s numerous benefits.

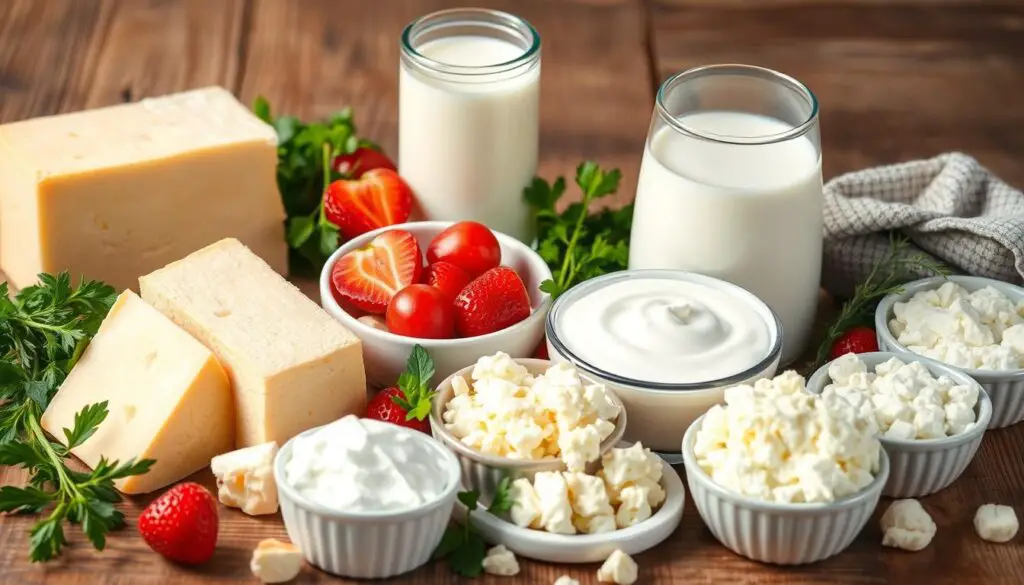
Dairy Products and Their Protein Content
Dairy products are renowned for their protein-rich composition, making them indispensable for a balanced diet and sustained energy. Notably, Greek yogurt and cottage cheese stand out as premier sources of healthy high-protein foods.
Greek Yogurt and Cottage Cheese Benefits
Greek yogurt, with its protein content of approximately 23 grams per serving, emerges as a superior choice for those in pursuit of a protein-rich snack or meal component. Conversely, cottage cheese, offering 11.1 grams of low-fat protein per half-cup, is another dairy giant. Both products are not only protein-dense but also rich in calcium and probiotics, contributing to enhanced health and wellness.
Lactose-Free Options
For those with lactose intolerance, a range of lactose-free protein foods is available, including lactose-free milk and plant-based dairy alternatives enriched with additional protein. These alternatives enable individuals with dietary limitations to partake in the nutritional advantages of dairy without the lactose-related discomfort.

“Dairy products are a fantastic source of high-quality protein, providing essential amino acids and supporting muscle growth and recovery.”
Incorporating protein-rich foods such as Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and lactose-free dairy options into a well-rounded diet is an effective strategy to fulfill protein requirements, enhance energy levels, and foster overall health and wellness.
Nuts and Seeds as Protein-Rich Snacks
In the realm of healthy high-protein snacks, nuts and seeds emerge as unparalleled nutritional powerhouses. These diminutive wonders not only offer a delightful textural contrast but also serve as a reservoir of protein, healthy fats, and vital vitamins and minerals.
Hemp seeds, a mere handful, yield an astonishing 9 grams of plant-based protein. Pumpkin seeds, similarly, contribute 8 grams of protein per 1-ounce serving. Peanuts, a staple in many diets, boast 7 grams of protein per ounce, positioning them as a prime choice for those seeking an energy-boosting protein supplement.
- Almonds: 6 grams of protein per 1-ounce serving
- Sunflower seeds: 6 grams of protein per 1-ounce serving
- Pistachios: About 6 grams of protein per serving
- Cashews: 5 grams of protein per 1-ounce serving
- Flaxseeds: Approximately 5 grams of protein per ounce
- Hazelnuts: Around 4 grams of protein per 1-ounce serving
- Walnuts: 4 grams of protein per 1-ounce serving
Integrating a diverse array of these high-protein snacks into your regimen can significantly enhance your satiety and energy levels. Whether your preference leans towards the crunch of almonds, the nuttiness of walnuts, or the protein-dense chia seeds, there exists a nutrient-dense alternative to cater to every palate.
“Nuts and seeds are a fantastic source of protein, healthy fats, and fiber, making them an excellent choice for a satisfying and nourishing snack.”
It is noteworthy that the daily protein requirement is approximately 50 grams. Thus, these high-protein snacks can be a crucial component of a well-rounded diet, aiding in the fulfillment of protein needs while also providing a surge of energy-boosting nutrients.

Eggs: The Complete Protein Package
Eggs stand out as a protein-packed food par excellence, boasting a complete amino acid profile. A single large egg, with its 6 grams of high-quality protein, emerges as a quintessential choice for protein foods for quick energy.
Nutritional Profile of Eggs
Eggs transcend their protein value, offering a spectrum of vital nutrients. A single large egg is replete with:
- 77.5 calories
- 5.3 grams of fat
- 186 milligrams of cholesterol
- Vitamins A, D, B12, and minerals like iron, phosphorus, and selenium
Moreover, eggs are a rich source of choline, an indispensable nutrient for brain health and development. They also contain lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that bolster eye health.
Ways to Incorporate Eggs in Your Diet
Eggs, with their versatility, can be seamlessly integrated into various meals to enhance your intake of healthy protein sources. Some straightforward methods include:
- Scrambled eggs with vegetables for a quick breakfast
- Hard-boiled eggs as a convenient on-the-go snack
- Frittatas or omelets packed with nutrient-dense ingredients
- Egg salad or deviled eggs for a protein-rich lunch
- Baked eggs nested in roasted vegetables for a satisfying dinner
Regardless of the preparation method, eggs represent a nutritious and affordable means to elevate your protein intake, thereby contributing to your overall health and wellness.

Legumes and Beans for Sustained Energy
Legumes and beans stand as formidable plant-based protein sources, delivering sustained energy throughout the day. These foods are replete with complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, positioning them as an exemplary choice for fueling the body and sustaining endurance over extended periods.
For example, a single cup of cooked lentils contains an impressive 18 grams of protein, rivaling the protein content of lean meats. Legumes such as chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans are also rich in protein for endurance, alongside a plethora of other nutrients.
Moreover, legumes and beans are characterized by their low fat content, high fiber, and low glycemic index. This profile aids in blood sugar regulation, providing a consistent energy flow rather than inducing spikes and crashes. Their inclusion in meals supports digestive health, aids in weight management, and enhances overall wellness.
Legumes and beans can be seamlessly integrated into various dishes, from soups and stews to salads and side dishes. Their adaptability makes them an ideal addition to diverse cuisines and dietary preferences, significantly contributing to protein foods for healthy skin and sustained energy levels.
“Legumes are a sustainable, affordable, and nutritious food that can play a key role in promoting health and energy levels.”

The spectrum of benefits offered by legumes and beans, from the humble lentil to the mighty chickpea, underscores their importance for overall well-being. By embracing these plant-based powerhouses, one can effectively fuel their body and maintain elevated energy levels throughout the day.
Protein Supplements and Powders
In the quest for a balanced diet and an active lifestyle, the popularity of protein supplements and powders has surged. These convenient additions to your nutrition regimen are particularly beneficial for athletes, fitness aficionados, or individuals with elevated protein requirements.
Whey, casein, soy, and pea protein are among the prevalent protein powder varieties. While whole foods are the preferred protein sources, supplements can assist in fulfilling daily protein needs and bolstering fitness objectives.
When selecting a protein powder, prioritizing a high-quality product from a trusted brand is crucial. Opt for powders with uncomplicated, natural ingredients, steering clear of those with excessive additives or artificial sweeteners. Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional can further elucidate the most suitable protein supplement quantity and type for your specific requirements.
Protein Powders for Energy and Performance
Protein shakes serve as a practical means to fuel workouts and support muscle recovery. The optimal best protein powder offers a concentrated amino acid source, pivotal for powering an active lifestyle and maintaining lean muscle mass.
- Whey protein isolate is frequently endorsed for its superior, easily digestible protein quality.
- Plant-based protein shakes for energy, such as those formulated with pea protein, present a vegetarian-friendly option.
- Integrating protein to fuel workouts into your regimen can facilitate attainment of fitness and body composition objectives.
It is important to note that while protein supplements are advantageous, they should not supplant a well-rounded, nutrient-dense diet. Engaging with a healthcare professional to ascertain the most effective strategy for your individual health and fitness aspirations is advisable.

“Protein powder should supplement three balanced, protein-rich meals over the course of a day,” advises registered dietitian Kaleigh Tjoelker.
Timing Your Protein Intake for Maximum Benefits
Optimizing the timing of your protein intake is crucial for maximizing its benefits in an active lifestyle. Consuming the appropriate amount of protein before and after workouts supports muscle recovery and growth. This ensures you have the energy to power through your fitness routine effectively.
Pre and Post-Workout Protein
It is advisable to have a protein-rich snack or meal within 30 minutes before your workout. This provides your muscles with the essential amino acids necessary for initiating the repair and growth process. Studies indicate that consuming approximately 30 grams of high-quality protein within two hours after exercise can further enhance muscle protein synthesis and support overall recovery.
Protein Distribution Throughout the Day
Instead of consuming all your daily protein in one or two large meals, consider distributing it evenly throughout the day. Research suggests that distributing your protein intake into smaller, more frequent servings (every 3-4 hours) may be more beneficial for muscle protein synthesis and maintaining steady energy levels. This approach helps prevent fatigue and supports an active lifestyle powered by a protein-rich diet.
| Body Weight | Recommended Daily Protein Intake |
|---|---|
| 100 pounds (45 kilograms) | 54 to 77 grams |
| 150 pounds (68 kilograms) | 82 to 116 grams |
| 200 pounds (91 kilograms) | 109 to 155 grams |
| 250 pounds (113 kilograms) | 136 to 192 grams |
By timing your protein intake for energy and distributing it throughout the day, you can optimize its benefits. This supports your active lifestyle and overall health.

Combining Protein Sources for Complete Nutrition
To achieve a balanced high-protein diet, it is imperative to amalgamate diverse protein sources. This ensures a comprehensive amino acid profile and a wide array of essential nutrients. By integrating animal-based proteins, such as chicken or fish, with plant-based alternatives, including quinoa, lentils, or beans, one can craft meals that are not only satiating but also nutritionally dense.
Adopting a varied approach to protein intake, encompassing lean meats, seafood, and plant-based powerhouses like tofu, tempeh, and edamame, can significantly enhance the interest and diversity of your protein diet plan. This strategy not only guarantees a complete amino acid spectrum but also offers a broader range of vitamins, minerals, and other health-promoting compounds. These elements are crucial for maintaining overall health and energy levels.
It is crucial to remember that a well-crafted high-protein diet plan must strike a balance between different protein sources. Additionally, it should be complemented by an abundance of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to fulfill your body’s nutritional requirements. By strategically combining complementary protein sources, one can devise a balanced high-protein meal plan that adequately fuels the body and sustains energy levels throughout the day.
FAQ
What are the essential amino acids and their functions?
Proteins, comprising 20 amino acids, are categorized into essential, nonessential, and conditional types. Essential amino acids, indispensable through dietary intake, are pivotal for hormone synthesis, muscle development, and immune system functionality.
How much protein do I need daily based on my age, sex, weight, and activity level?
Protein requirements are age, sex, weight, and activity level-dependent. Adults generally require 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, active individuals, pregnant women, and older adults may require higher protein intake.
What are the benefits of a high-protein diet?
High-protein diets enhance satiety, aid in weight management, and lower the risk of hypertension. They also facilitate injury recovery and mitigate sarcopenia risk. Additionally, protein intake is linked to reduced muscle loss and preserved cognitive function.
What are some examples of animal-based and plant-based protein sources?
Animal-based proteins include lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs. Legumes, tofu, and soy products represent plant-based options. Dairy and its alternatives, such as Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, are also rich in protein.
What are the health benefits of incorporating lean meats and poultry into my diet?
Lean meats and poultry serve as high-quality protein sources, delivering essential nutrients like zinc and iron. Their inclusion in meals aids in maintaining energy and supports muscle health.
How can I get the benefits of fish and seafood in my diet?
Fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon, is a protein-rich food that also provides heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Consuming fish at least twice weekly adds protein variety and supports health. Opting for sustainable seafood options protects marine ecosystems while offering nutritional benefits.
What are some plant-based protein sources I can incorporate into my diet?
Legumes, tofu, tempeh, and seitan are plant-based proteins rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They support muscle growth, weight management, and overall health. Combining different plant proteins ensures a complete amino acid profile for vegetarians and vegans.
What are the benefits of incorporating dairy products into my high-protein diet?
Dairy products, especially Greek yogurt and cottage cheese, are high in protein, calcium, and probiotics. For those with lactose intolerance, lactose-free milk and plant-based alternatives fortified with protein are viable alternatives.
How can nuts and seeds contribute to my protein intake?
Nuts and seeds, being nutrient-dense snacks, provide protein, healthy fats, and fiber. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds are excellent choices. They help manage hunger, body weight, and prevent fatigue when part of a balanced diet.
What are the benefits of incorporating eggs into my meals?
Eggs, being a complete protein source, offer all essential amino acids. They are versatile and can be incorporated into various meals, providing vitamins and minerals like vitamin D and choline. Eggs are an easy way to boost protein intake throughout the day.
How can legumes and beans support my energy levels?
Legumes and beans are excellent plant-based protein sources that provide sustained energy. They are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, supporting digestive health, weight management, and offering long-lasting energy throughout the day.
When is the best time to consume protein, and how should I distribute it throughout the day?
Consuming protein before and after workouts supports muscle recovery and growth. Distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day, rather than consuming it all at once, may be more beneficial for muscle protein synthesis. Aim for protein-rich meals and snacks every 3-4 hours to maintain steady energy levels and support overall health.
How can I ensure I’m getting a balanced, high-protein diet?
Combining different protein sources ensures a complete amino acid profile and varied nutrient intake. Mix animal and plant-based proteins, such as chicken with quinoa or lentils with rice. This approach provides a range of essential nutrients and can make meals more interesting and satisfying. A balanced high-protein diet should include a variety of protein sources along with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for optimal nutrition.






